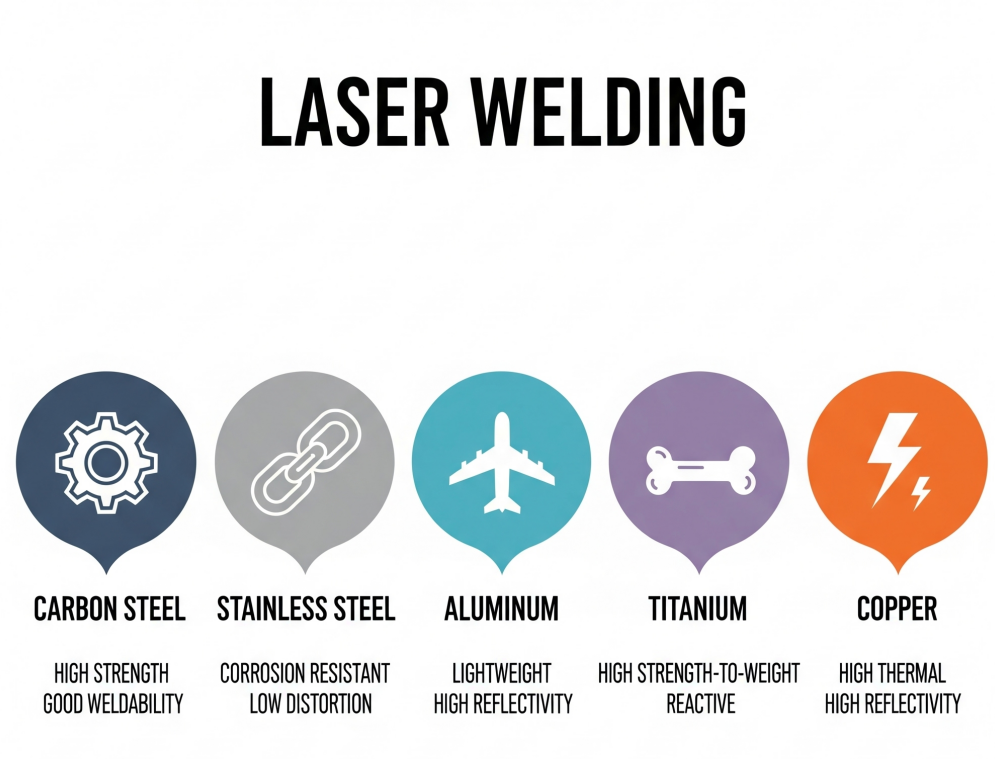
A metal’s success with laser welding hinges on its core physical properties. For instance, high reflectivity can deflect the laser’s energy, while high thermal conductivity dissipates heat too quickly from the weld zone. These characteristics, along with the melting point, determine how efficiently a material absorbs energy to form a strong, precise weld.
Here’s a breakdown of the common metals and how their properties come into play.
Laser Welding Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is an iron-carbon alloy with up to 2.1% carbon content. The carbon content is the primary determinant of its properties.
Low-carbon steel (less than 0.25% carbon) is ductile, tough, and easily machinable and weldable. It’s often used for body panels, wire, and pipes.
Medium-carbon steel (0.25% to 0.60% carbon) is stronger and harder than low-carbon steel. This makes it suitable for components that require more strength and wear resistance, such as gears, shafts, and railway wheels.
High-carbon steel (more than 0.60% carbon) is the strongest and hardest of the three, but it is also the least ductile and most brittle. Its hardness makes it ideal for cutting tools, springs, and high-strength wires, but it requires careful handling during welding to prevent cracking.
Carbon steel is a workhorse in manufacturing, and it takes to laser welding beautifully.
Advantages: You get strong, deep welds with amazing precision and very little distortion. The speed is a massive plus, boosting productivity on the factory floor.
Considerations: The rapid cooling of the laser process can make the weld brittle and prone to cracking. Sometimes, preheating the part is necessary to slow the cooling and prevent issues.
Laser Welding Stainless Steel
This is a match made in heaven. Laser welding is the perfect process for stainless steel, especially for industries that demand cleanliness.
Advantages: The low, focused heat input is a huge win. It preserves the corrosion-resistant properties of stainless steel by preventing something called “carbide precipitation.” This results in surgically clean and precise welds, which is why it’s so popular in the medical and food industries.
Considerations: Most common stainless steels, like the 300 series (e.g., 304, 316), weld exceptionally well. However, some other grades, like the 400 series, can become brittle in the heat-affected zone.
Laser Welding Aluminum
Welding aluminum has always been tricky, but laser welding is changing the game.
Advantages: Aluminum is a great heat conductor, which means with traditional welding, the heat spreads out and causes the whole part to warp. The laser’s focused energy and low heat input solve this problem, dramatically reducing distortion.
Considerations: Aluminum is highly reflective. The shiny surface can bounce the laser beam right off. Success depends on a few key things: spotless surface cleaning, the right shielding gas, and using the right kind of laser (fiber lasers are often preferred) to ensure the energy gets absorbed.
Laser Welding Titanium
If you need to weld titanium, a laser is one of your best tools for the job.
Advantages: Titanium is a reactive metal, meaning it easily gets contaminated by oxygen in the air when it’s molten, leading to a weak, brittle weld. The laser’s speed and precision minimize the time the metal is molten and exposed, reducing the risk of contamination and embrittlement.
Considerations: Just like with TIG welding titanium, you still need to be extremely careful. Absolute cleanliness and perfect shielding with an inert gas (like argon) are non-negotiable.
Laser Welding Copper and Other Reflective Metals
This is where laser welding pushes the boundaries of what’s possible.
Advantages: A laser welding machine can join highly reflective materials like copper, which are incredibly difficult to weld with almost any other method. This is critical for applications like electric vehicle (EV) batteries, where copper and aluminum must be joined.
Considerations: This is expert-level stuff. The high reflectivity and thermal conductivity can actually damage the laser’s optics if not managed correctly. It often requires specialized equipment, along with advanced techniques.
What Are the Limitation of Laser Welding?
While it sounds like a miracle tool, it’s not perfect for every job. It’s important to understand the trade-offs.
1.High Initial Cost: A professional laser welding machine is a significant investment, much more expensive than traditional MIG or TIG setups.
2.Strict Joint Requirements: As mentioned, lasers need a near-perfect fit. If your parts have gaps or aren’t cut precisely, the laser won’t be able to bridge them effectively.
3.Reflectivity Issues: Shiny materials like aluminum and copper can be tough to weld without specialized lasers and techniques.
4.Safety Concerns: The high-intensity laser beam is extremely dangerous and can cause severe eye injury and skin burns, even from reflections. Proper safety enclosures and personal protective equipment (PPE) are absolutely mandatory.
Best Practices for Flawless Laser Welds
To get the most out of your laser welding process, you need to nail the fundamentals.
Preparation is Everything
Joint Fit-Up: We can’t say it enough: your parts must fit together tightly. Aim for a gap of less than 10% of the material’s thickness for the best results.
Surface Cleaning: Get rid of everything that isn’t metal. This means removing all oils, grease, oxides, and any other contaminants. A clean surface is essential to prevent pores and other defects in your weld.
Control Your Process
Shielding Gas: Just like TIG and MIG, laser welding uses an inert gas (usually argon or helium) to shield the molten weld pool from oxygen and nitrogen in the air, ensuring a strong, clean weld.
Parameter Optimization: You have to dial in your settings. Laser power, welding speed, and focus distance must be perfectly calibrated for the specific material and thickness you’re working with.
Safety First, Always
Laser welding isn’t a process you can be casual about. The focused light is incredibly powerful. Anyone near the operation must wear specialized laser safety glasses rated for the specific wavelength of your laser.
Is a Laser Welding Machine the Right Choice for You?
So, should you invest in laser welding?
Let’s recap. Laser welding is an advanced manufacturing tool that delivers unparalleled speed, precision, and quality. The trade-off is the high initial cost and the strict requirements for clean, well-fitting parts.
Our final thought: If your work demands high volume, automation, and pinpoint accuracy—especially on delicate or challenging materials—then laser welding isn’t just another option. It’s the superior solution that can revolutionize your production.
Post time: Aug-15-2025